The construction industry has long been a pillar of global economic development, but despite its significance, it has also faced many challenges. Issues like inefficiency, waste, labor shortages, and high costs have plagued the sector for decades. However, in recent years, an innovative technology has emerged with the potential to transform the construction process: 3D printing. Often referred to as additive manufacturing, 3D printing in construction is enabling faster, cheaper, and more sustainable methods of building structures, from homes to skyscrapers. This article will explore how 3D printing is revolutionizing the construction industry, addressing its applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of construction.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing in construction enables the creation of buildings and components layer by layer, offering faster, cheaper, and more sustainable alternatives to traditional construction methods.
- The benefits of 3D printing in construction include cost reduction, speed, design flexibility, and waste reduction.
- Despite its promise, challenges remain, such as material limitations, regulatory hurdles, and the need for more advanced printing technology.
- As technology improves and becomes more widespread, 3D printing is expected to play a central role in addressing the housing crisis and revolutionizing infrastructure projects worldwide.
What is 3D Printing in Construction?
3D printing in construction refers to the process of using a printer to create buildings, structures, and components layer by layer based on a digital model. Unlike traditional construction methods, which rely on subtractive techniques (cutting, chiseling, or digging), 3D printing builds objects from scratch by adding material, typically concrete, plastics, or metals, layer by layer.
3D printing can be applied to a variety of construction tasks, such as:
- Printing entire buildings: Full-scale homes or commercial structures can be printed.
- Building components: Items like walls, columns, beams, or roofs can be printed.
- Infrastructure: Bridges, tunnels, and other types of infrastructure can also benefit from 3D printing.
This transformative technology uses a range of 3D printing techniques, including concrete printing, metal printing, and plastic filament-based printing, each suited to different aspects of construction.
How Does 3D Printing Work in Construction?
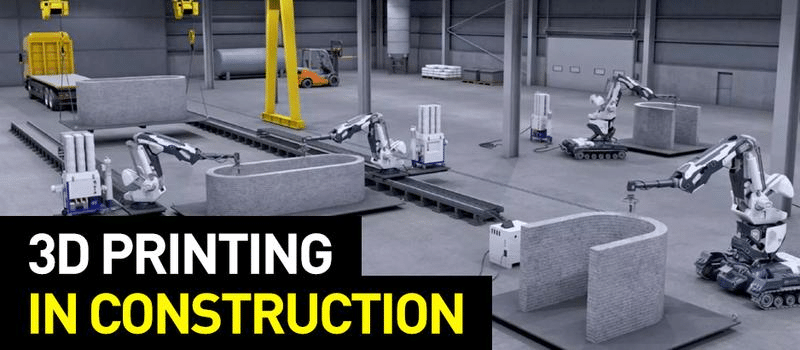
3D printing in construction works similarly to traditional 3D printing but with the use of larger, more robust machines. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
- Digital Design: The first step involves creating a 3D model of the building or component using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is crucial as it dictates the size, structure, and details of the printed object.
- Preparation of Materials: The material for printing, which can range from concrete to advanced polymer blends, is loaded into the 3D printer. For construction, special materials are often used to ensure durability, insulation, and weather resistance.
- Layer-by-Layer Printing: The 3D printer extrudes the material layer by layer according to the digital blueprint. Each layer is carefully placed on top of the previous one, allowing the printer to build up the structure gradually.
- Finishing Touches: After printing, the structure may require additional finishing work, such as installing plumbing, electrical systems, or insulation. However, much of the basic structure will be complete.
Applications of 3D Printing in Construction
The potential applications of 3D printing in construction are vast and continue to grow as the technology matures. Some of the most notable applications include:
1. Affordable Housing
One of the most exciting uses of 3D printing is its potential to address the global housing crisis. Traditional home construction can be expensive, often requiring extensive labor, materials, and time. 3D printing offers a solution by drastically reducing the cost of construction while speeding up the process. Homes can be printed in a matter of days at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods.
2. Sustainable Building Materials
3D printing allows for the use of sustainable building materials, such as recycled plastics or concrete mixed with biodegradable elements. This not only helps in reducing waste but also minimizes the carbon footprint of construction projects.
3. Customization and Design Flexibility
With 3D printing, architects and designers are no longer constrained by traditional building methods. Custom designs, organic shapes, and intricate structures are easier to produce with 3D printers. This opens up opportunities for creating innovative and unique architectural styles that would have been difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional construction techniques.
4. Building Large Infrastructure
3D printing is not limited to small buildings or homes. It has shown great promise in large-scale infrastructure projects, such as bridges and tunnels. The ability to print large concrete structures on-site can reduce costs and enhance the speed of construction.
5. Construction of Complex Components
3D printing is used to produce highly complex building components, such as custom facades, detailed reinforcement parts, or unique architectural elements. These components can be designed precisely to meet specific needs, helping to streamline the construction process.
6. Rapid Prototyping
Before commencing large-scale construction projects, 3D printing can be used for rapid prototyping of models. This enables architects, engineers, and clients to visualize and test designs before committing to full-scale construction.
7. On-Demand Construction
One of the most groundbreaking aspects of 3D printing in construction is its ability to produce materials on demand. For remote locations or emergency situations, construction teams can deploy portable 3D printers to print building components directly at the construction site, eliminating the need for transportation and reducing delays.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Construction
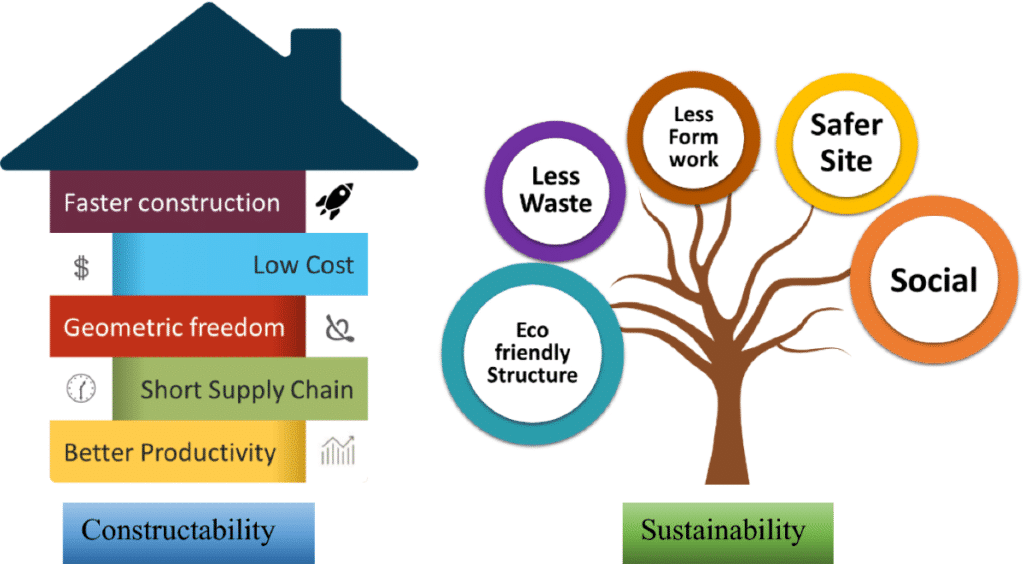
The integration of 3D printing into construction has unlocked several key benefits:
1. Cost Reduction
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in construction is the reduction in costs. With fewer materials, less labor, and the reduction of errors in construction, the cost of building can be significantly reduced. Additionally, construction times are reduced, saving money in the long run.
2. Speed
3D printing can dramatically accelerate the construction process. While traditional construction can take months or even years to complete, 3D printing allows for the creation of entire buildings or structures within days. This speed is particularly useful in emergency situations or for rapid housing needs in developing regions.
3. Waste Reduction
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process, which means it only uses the exact amount of material needed to build the structure. This minimizes waste production, making the process more environmentally friendly than traditional methods.
4. Design Flexibility
3D printing enables architects and engineers to design buildings that would otherwise be challenging or costly to construct. The flexibility of the technology allows for greater creativity in design, enabling the creation of structures that push the boundaries of traditional construction.
5. Labor Efficiency
With automated printing, the need for human labor is significantly reduced. Workers focus on overseeing and maintaining the 3D printers, freeing up resources for other important tasks. The efficiency of the process reduces the number of workers needed on-site, and as the technology becomes more accessible, it can help address labor shortages in construction.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Construction
Despite the numerous benefits, 3D printing in construction faces several challenges:
1. Material Limitations
The variety of materials available for 3D printing in construction is still limited compared to traditional building materials. Though concrete and plastics are common, other materials like steel, wood, or glass are still under research for use in 3D printing.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
Building codes and regulations are a challenge for 3D printed structures. Since 3D printing is a relatively new technology, many regulatory bodies have not yet developed standardized codes that account for the unique properties of 3D printed buildings. This creates uncertainty for contractors and developers.
3. Initial Investment Costs
The initial investment required for a 3D printing machine can be quite high, making it a barrier for smaller construction companies. However, the costs are expected to decrease as the technology becomes more widespread and refined.
4. Limited Large-Scale Printing
While 3D printing has advanced rapidly, there are still limitations when it comes to printing very large-scale structures, such as multi-story buildings. Improvements in printing technology are required before large, complex structures can be fully printed.
The Future of 3D Printing in Construction: Emerging Trends and Technologies
- This topic could explore the newest advancements in 3D printing technology for construction, including the use of robotics, artificial intelligence, and new materials like bio-concrete, self-healing materials, and smart polymers.
- Subtopics: Integration with AI for predictive modeling, the role of robotics in 3D printing, emerging printing technologies (e.g., concrete printers vs. metal printers), future material science in 3D printing.
How 3D Printing is Shaping the Sustainability of Urban Development
- Focus on how 3D printing can help cities become more sustainable, looking at energy-efficient homes, the reduction of waste in construction, and how it can address the environmental impact of traditional building methods.
- Subtopics: Environmental benefits, reducing carbon footprints, low-waste construction, eco-friendly materials, and energy-efficient 3D printing techniques.
The Role of 3D Printing in Affordable Housing and Homelessness Solutions
- Discuss how 3D printing could be a solution to the global affordable housing crisis and homelessness by offering rapid construction of low-cost housing units, as well as the potential for nonprofit organizations to adopt the technology.
- Subtopics: Non-profit organizations using 3D printing, modular 3D printed homes, disaster relief housing, international examples of affordable housing projects.
3D Printing and the Reshaping of Building Materials: Innovations and Challenges
- Dive deep into the innovative materials being used for 3D printing in construction, such as advanced concrete, composites, and alternative materials like recycled plastics, and the challenges of material durability, cost, and sourcing.
- Subtopics: Material research for 3D printing, new concrete mixtures for printing, sustainable building materials, challenges with material quality and sourcing.
The Economic Impact of 3D Printing in Construction: Cost Savings and Market Growth
- Analyze the economic implications of 3D printing in the construction sector, including long-term cost savings, new business models, and how the technology could affect the job market for laborers, architects, and engineers.
- Subtopics: Economic growth of 3D printing construction companies, the reduction of labor costs, the impact on traditional construction jobs, cost-saving examples from projects.
Designing for 3D Printing: How Architects Are Adapting to New Technology
- Explore how the role of architects is changing with the introduction of 3D printing in construction, including how architects can design for the capabilities of 3D printing and collaborate with engineers to optimize designs for 3D printing.
- Subtopics: How architectural design is evolving, software tools for 3D printing, collaboration between architects and engineers, new creative design possibilities.
Read More – Biotechnology In Agriculture: Innovations For A Greener Future
Conclusion
3D printing is reshaping the construction industry, offering solutions to some of its most persistent challenges, including high costs, inefficiencies, and waste. With its ability to produce customized, sustainable, and affordable buildings, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about construction. As the technology continues to evolve, it will likely play an even more significant role in shaping the future of the built environment.
FAQs
1. What materials are used in 3D printing construction?
Materials used in 3D printing construction typically include concrete, polymers, metals, and composites. Researchers are continually exploring new materials to improve strength, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
2. How long does it take to print a house with 3D technology?
It can take as little as 24 hours to print the basic structure of a house, depending on the size and complexity of the design. However, finishing touches like electrical systems and interiors take longer.
3. Is 3D printing safe for construction?
Yes, 3D printing has been shown to produce strong and durable structures when proper materials and designs are used. However, regulatory approvals and adherence to building codes are still necessary to ensure safety.
4. Can 3D printing be used for commercial buildings?
Yes, 3D printing has already been used for small-scale commercial buildings. As technology advances, larger and more complex commercial projects will become feasible.
5. How does 3D printing reduce construction costs?
3D printing reduces costs by lowering labor needs, reducing material waste, and accelerating construction timelines. Additionally, on-site printing eliminates transportation costs for materials.
6. Can 3D printing help solve the housing crisis?
Yes, 3D printing has the potential to drastically reduce the cost and time required to build affordable housing, addressing the global housing shortage.
7. What are the environmental benefits of 3D printing in construction?
3D printing reduces material waste, energy consumption, and the overall environmental impact of construction projects. Additionally, sustainable materials can be used to create eco-friendly buildings.